Fibroids are one of the leading cause of infertility.
Fibroids are non-cancerous abnormal growths that develop on or in the uterus of a woman’s uterus. There are many procedures available to cure this problem, which includes both the surgical and nonsurgical method
One of the most advanced surgical techniques is LAAM (Laparoscopic Assisted Abdominal Myomectomy).
Here in our clinic – one of the topmost IVF specialists in Gurgaon India – we provide the latest treatment options. We provide all details about LAAM and how it can help in removing fibroids.
Below, we talk about LAAM and its advantages over other surgical methods and what makes it a safer technique.
What is LAAM?

LAAM is a type of hybrid technique ( the mixture of 2 technologies) that uses the best elements of the following technologies:-
- Laparoscopy
- Traditional myomectomy
The resulting technology is called LAAM.
The LAAM method requires just two tiny cuts for the surgery, one of 5 mm incision at the belly button and the other in the form of 3 cm incision at the bikini line.
This makes LAAM one of the least invasive and safest methods for removing fibroids.
How are fibroids linked to infertility? What signs does a woman look for?
Myomectomy is performed to remove the fibroids from the uterus so that the female can conceive as the embryo is transplanted in the uterus, and it has a crucial role in pregnancy.
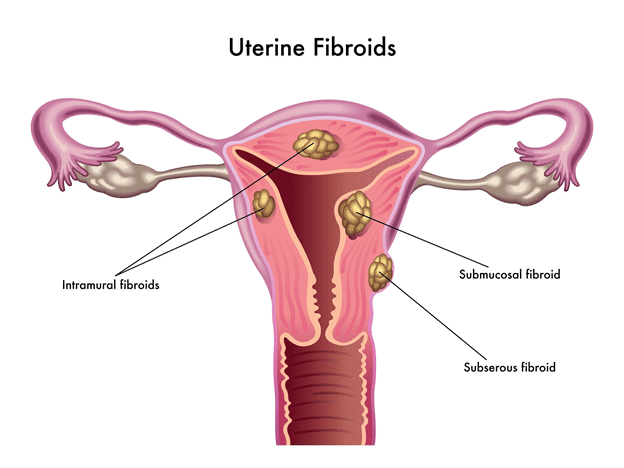
Types of fibroids:
- Submucosal fibroids
- Intramural fibroids
- Subserosal fibroids
Out of these, the first two types of fibroids should be removed as they increase the chance of miscarriage and cause difficulty in conceiving.
Symptoms:
- abnormal bleeding
- pain in lower stomach
- Contraction of fibroids against the bladder and back.
Who needs LAAM Myomectomy?
- Women who are past childbearing and suffer from fibroids,
- Women with fibroids which have created extensive distortion to the uterus
- Women who are menopausal can’t undergo LAAM.
The process of LAAM Myomectomy:-
Patients are evaluated before surgery to ensure that the right procedure is matched to the patient.
- ultrasound
- Laboratory evaluation
- Types of surgical procedure for myomectomy: Only in those cases, the LAAM Myomectomy will be performed in which the patient is found to be suitable for the surgery. The patient’s uterus must be capable of being repaired after the fibroid removal, as for some females the damaged caused by the fibroids is too extensive.
- Surgery: during the surgery to avoid the blood loss, in the process a permanent or temporary blockage of the uterine artery is done before removal of the fibroids allows for excellent control of bleeding. This provides a controlled elimination of fibroids.
Why choose LAAM over other procedure?
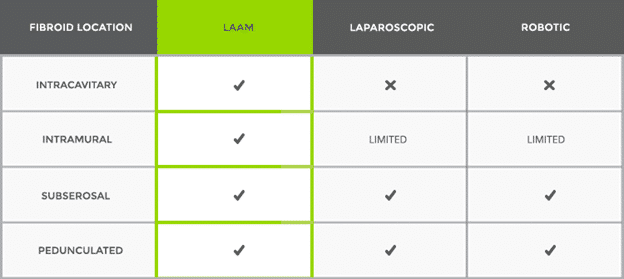
LAAM has many advantages over other Like Laparoscopic surgical treatments.
Open myomectomy:
Open methods are still the most commonly performed since with this approach all fibroids can be removed in all locations. The significant disadvantages of:
The open approach are:
- A much larger incision,
- More pain
- Extended recovery periods of 6 to 8 weeks.
- There is a much higher rate of complexities as well.
- Open surgical myomectomy procedures increase the need for higher hospitalization.
Standard And Robotic Laparoscopic Approaches:-
- The procedural time is far too long
- larger fibroids include the cavity are much harder to remove
- The potential for heightened risk of uterine rupture during pregnancy.
- Higher blood loss.
Advantages Of LAAM Myomectomy:
- Elimination of fibroids of any size
- removal of fibroids irrespective of its location in patients;
This process even applies to patients with:-
- Earlier surgery,
- overweight patients
- patients with many fibroids in the uterus
- Excellent control of blood loss and after the method;
- restore the uterus with the use of the suitable technique, securing the best possible and efficient uterine muscle closure;
- The capability to “feel” the uterus for fibroids, providing for removal in most cases of all the fibroids present;
- Discharge from the hospital the same day of operation, including the ability to return to work in 10 to 14 days;
- least painful
- recovery time






